프록시 패턴은 어떤 객체에 대한 접근을 제어하기 위한 용도로 대리인이나 대변인에 해당하는 객체를 제공하는 행동 패턴이에요.
원격, 가상, 보호, 캐싱, 로깅 프록시와 같이 다양한 종류가 있어요. 이런 프록시들의 목적을 하나로 요약하면 자원 접근 제한 및 통제에요. 대표적인 예로 자바나 자바스크립트의 Class로 만든 Instance의 자원 접근을 Proxy를 통해서 부가 적인 기능을 수행할 수 있게 만드는 것이에요.
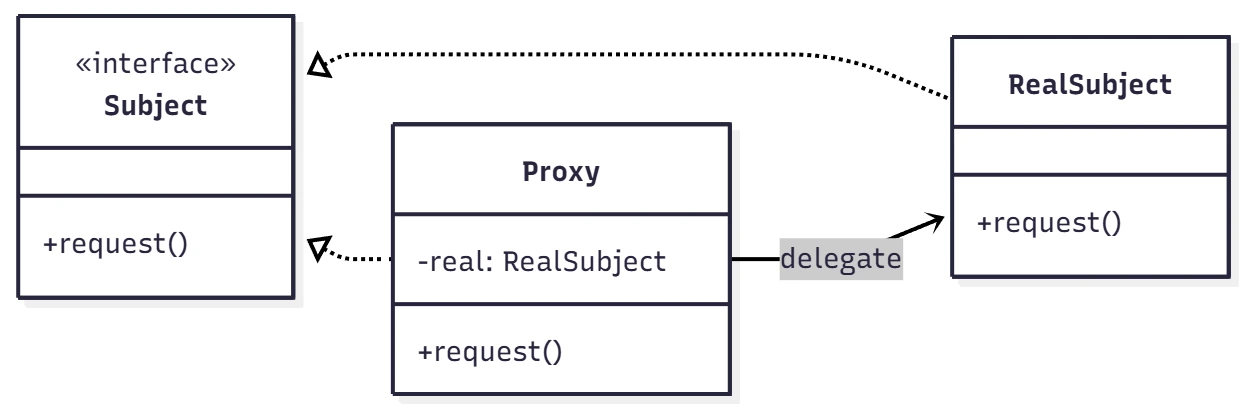
프록시는 특정 객체에 대한 접근 제어를 하기 위해 사용되고 특정 객체는 Subject라고 해요. 프록시(Proxy)는 Subject 인터페이스를 따라 구현하여 실제 RealSubject와 완전히 호환되도록 바꿀수 있어요.
이렇게 구현하면 Client가 사용할 때 기존의 Subject 인터페이스를 그대로 사용하며 Proxy가 어떻게 생겼는지 몰라도 사용할 수 있어요.
Subject : RealSubject가 구현하는 인터페이스에요. 아마 프록시를 추가한다는 것은 이미 Subject가 있을 확률이 높을 거라 생각해요.
RealSubject : 접근 제어할 원본 객체이며, 실제 핵심 작업을 수행하는 객체에요.
Proxy : RealSubject에 대한 접근을 제어할 중개자(대리인)
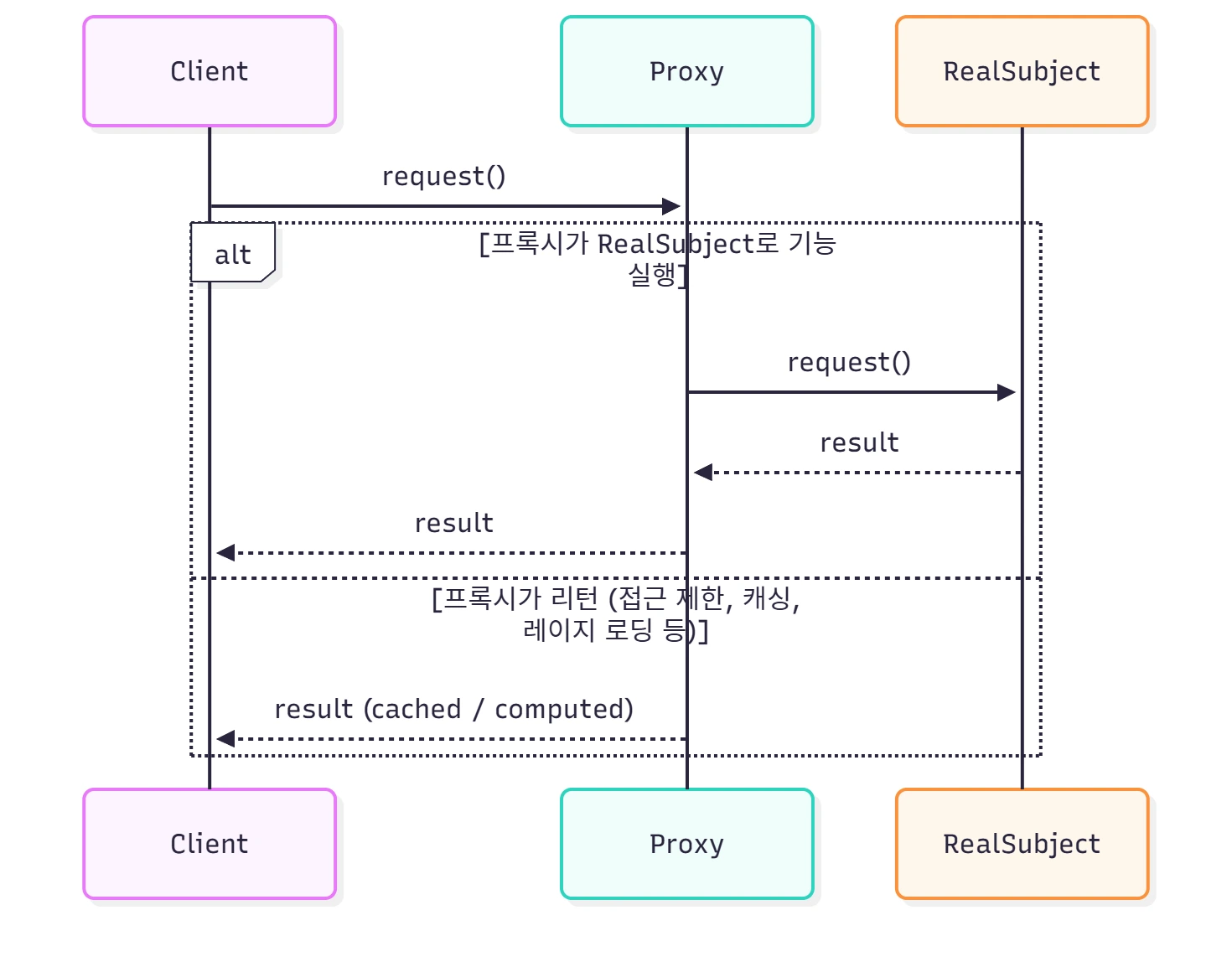
위 그림은 실제 Client가 Proxy 패턴으로 코드를 사용하면 어떤 순서로 코드가 실행될 지 보여줘요. Proxy의 request() 메서드를 사용하면, RealSubject의 알고리즘을 대신 위임하여 사용하고 그 값을 리턴해주거나 자체적으로 기능을 추가적으로 실행하거나 접근을 제한할 수 있어요.
프록시의 종류는 되게 다양해요. 여기서는 가상, 보호, 원격 프록시만 설명하도록 할게요.
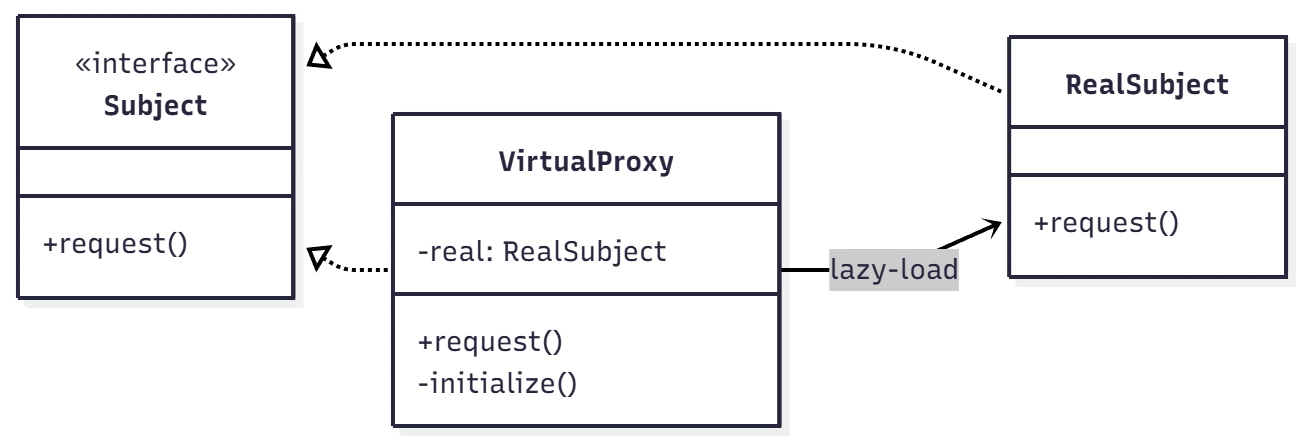
가상 프록시는 무거운 객체를 실제 요청 시점에 로딩하는 경우 사용해요. 보통 RealSubject 인스턴스 생성이 되지 않아 null일 경우 initialize() 함수를 통해 생성이 완료되도록 해요. 즉, 무거운 객체의 생성 시점을 필요한 시점으로 제어할 수 있어요.
// 2. 가상 프록시 (Virtual Proxy)// 무거운 객체의 생성을 실제 사용 시점까지 지연class HeavyImage { constructor(filename) { this.filename = filename; console.log(`[Heavy Object] "${filename}" 로딩 시작... (무거운 작업)`); // 실제로는 대용량 이미지 처리 등 this.data = `${filename}의 대용량 데이터`; console.log(`[Heavy Object] "${filename}" 로딩 완료!`); } display() { console.log(`[Heavy Object] 이미지 표시: ${this.filename}`); }}class VirtualImageProxy { constructor(filename) { this.filename = filename; this.realImage = null; console.log(`[Virtual Proxy] "${filename}" 프록시 생성 (실제 객체는 아직 생성 안됨)`); } display() { // 실제로 사용할 때 객체 생성 (Lazy Initialization) if (!this.realImage) { console.log(`[Virtual Proxy] 이제 실제 객체를 생성합니다`); this.realImage = new HeavyImage(this.filename); } this.realImage.display(); }}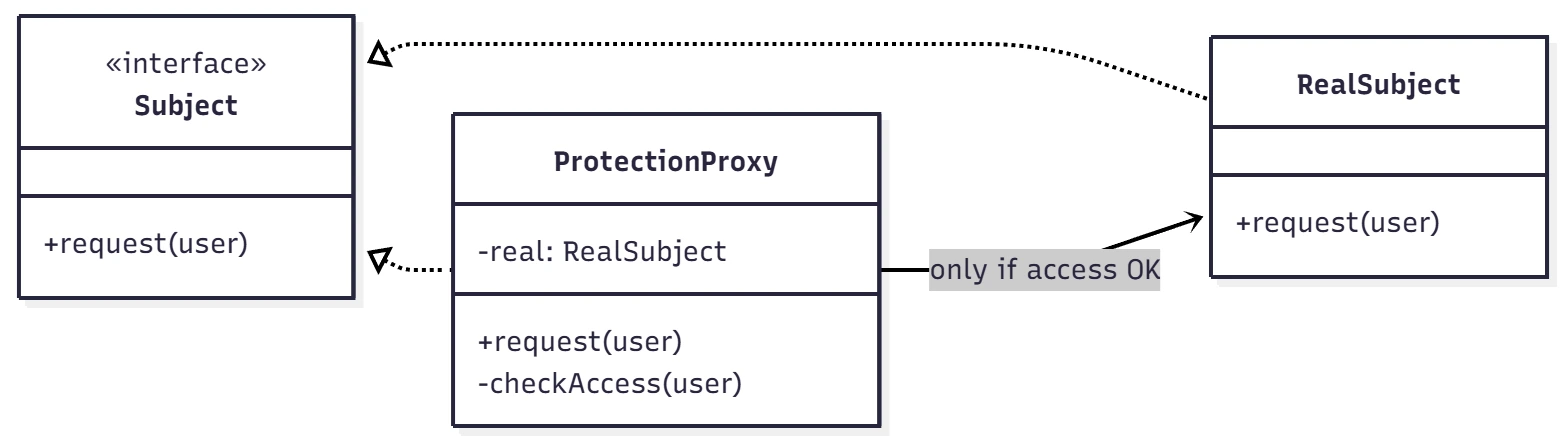
proxy가 RealSubject의 request요청을 하기 전에 checkAccess 메서드를 통해 접근을 제어할 수 있도록 해요. 보통 보안 목적을 위해 사용하는 경우가 많아요.
// 3. 보호 프록시 (Protection Proxy)// 접근 권한에 따라 객체 접근을 제어class BankAccount { constructor(owner, balance) { this.owner = owner; this.balance = balance; } deposit(amount) { this.balance += amount; console.log(`[계좌] ${amount}원 입금. 잔액: ${this.balance}원`); } withdraw(amount) { if (this.balance >= amount) { this.balance -= amount; console.log(`[계좌] ${amount}원 출금. 잔액: ${this.balance}원`); return true; } console.log(`[계좌] 잔액 부족`); return false; } getBalance() { return this.balance; }}class BankAccountProxy { constructor(account, currentUser) { this.account = account; this.currentUser = currentUser; } deposit(amount) { console.log(`[프록시] ${this.currentUser}가 입금 시도`); // 누구나 입금 가능 return this.account.deposit(amount); } withdraw(amount) { console.log(`[프록시] ${this.currentUser}가 출금 시도`); // 소유자만 출금 가능 if (this.currentUser === this.account.owner) { return this.account.withdraw(amount); } else { console.log(`[프록시] 권한 없음! ${this.currentUser}는 출금할 수 없습니다.`); return false; } } getBalance() { console.log(`[프록시] ${this.currentUser}가 잔액 조회 시도`); // 소유자만 잔액 조회 가능 if (this.currentUser === this.account.owner) { return this.account.getBalance(); } else { console.log(`[프록시] 권한 없음! 잔액 조회 불가`); return null; } }}// Clientconst account = new BankAccount('김철수', 10000);const ownerProxy = new BankAccountProxy(account, '김철수');console.log(`잔액: ${ownerProxy.getBalance()}원\n`); // 성공const strangerProxy = new BankAccountProxy(account, '홍길동');strangerProxy.getBalance(); // 실패 (권한 없음) 홍길동 != 김철수이기 때문.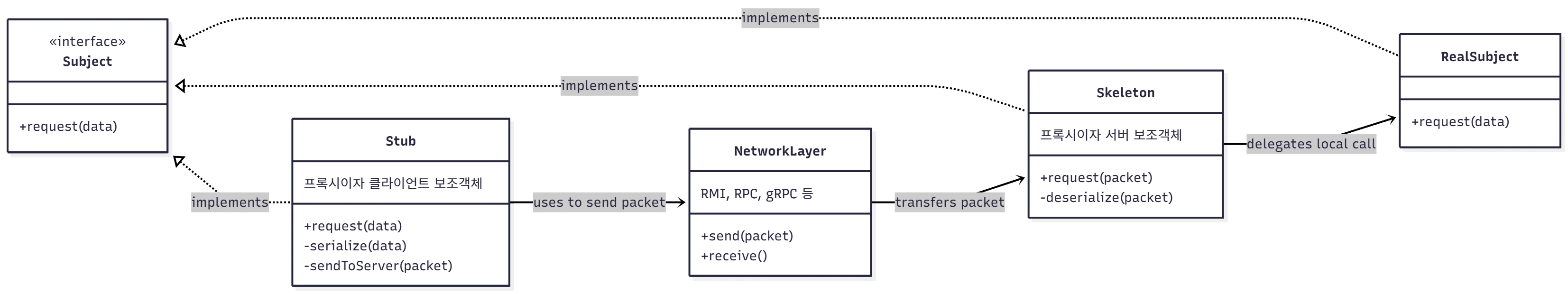
프록시가 중개할 대상 객체(RealSubject)가 다른 공간(네트워크)에 존재하는 경우에 주로 사용해요. 위 클래스 다이어그램은 사실 말이 안되는 다이어그램 이에요. 하지만 굳이 위 그림을 사용한 이유는 Client Proxy와 Server Proxy를 통해서 Server-Client간의 네트워크 위임을 하고 있다는 것을 나타내고 싶었어요.
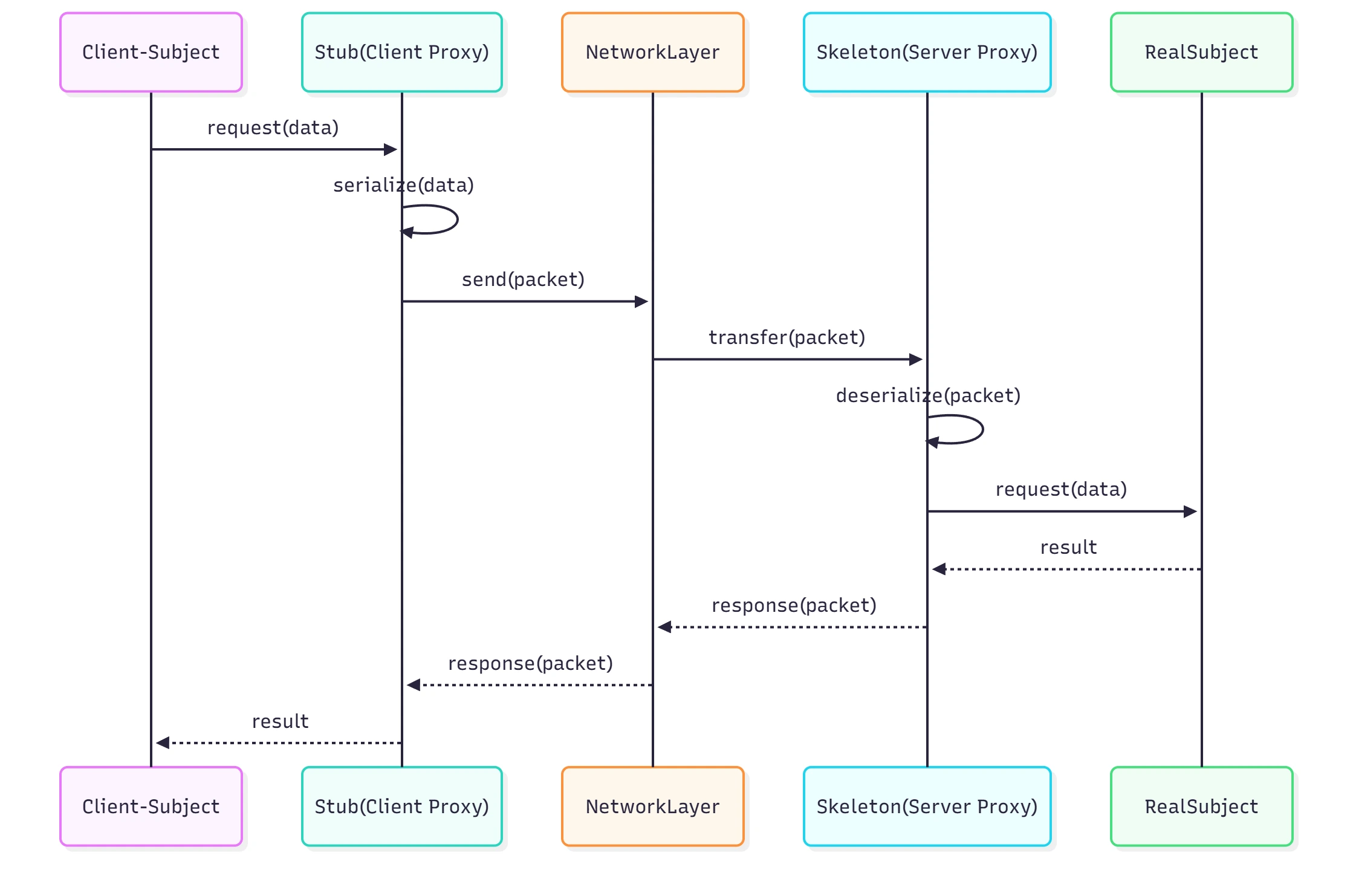
시퀀스 다이어그램을 통해서 보면 클라이언트든 서버든 결국 Subject 인터페이스를 따라 사용한다는 것을 알 수 있어요. 다만 중간에 Proxy가 추가되어 네트워크 통신을 하여 다른 공간의 객체를 사용할 수 있게 된거에요
// 원격 프록시 (Remote Proxy)// 원격 서버의 리소스를 로컬에 있는 것처럼 사용class ImageService { loadImage(imageId) { console.log(`[실제 서버] 이미지 ${imageId} 로딩 중...`); // 실제로는 fetch 등으로 서버와 통신 return `image_data_${imageId}`; }}class ImageServiceProxy { constructor() { this.imageService = new ImageService(); } loadImage(imageId) { console.log(`[프록시] 이미지 ${imageId} 요청 받음`); // 원격 서버에 요청 console.log(`[프록시] 서버에 요청 전달`); const imageData = this.imageService.loadImage(imageId); return imageData; }}에디터에 이미지 파일 또는 URL을 넣으면 이미지를 에디터에서 보여주는 기능이 이미 있다고 가정해요. 그런데 파일을 넣어서 이미지를 보여주는 경우에는 이미지 파일을 서버에 업로드까지 하는 기능이 필요하고, 특정 확장자의 이미지만 보여줄 수 있도록 만들고 싶다는 요구사항이 생겼어요. 이걸 프록시를 추가하여 해결할 경우 아래와 같은 코드가 나올 것 같아요.
// Client 코드, Config를 통해 이미지 업로드 세부 설정.const newEditor = createEditor({ uploadConfig: { uploadUrl: 'https://api.example.com/upload', allowedExtensions: ['jpg', 'jpeg', 'png', 'gif'], maxFileSize: 2 * 1024 * 1024, onUploadStart: () => { setUploading(true); addLog('파일 업로드 시작...', 'info'); }, onUploadSuccess: (url) => { setUploading(false); addLog(`업로드 성공: ${url}`, 'success'); }, onUploadError: (error) => { setUploading(false); addLog(`업로드 실패: ${error}`, 'error'); } }});// 에디터 생성 함수function createEditor(options = {}) { let imageHandler = new BasicImageHandler(); imageHandler = new ImageUploadProxy(options.uploadConfig, imageHandler); return new Editor(imageHandler);}// 기본 이미지 핸들러class BasicImageHandler { async handle(input) { console.log('[BasicHandler] input 받음:', input instanceof File ? input.name : input); // URL이면 그대로 반환 if (typeof input === 'string') { console.log('[BasicHandler] URL 그대로 반환'); return input; } // File이면 데이터 URL로 변환해서 반환 if (input instanceof File) { console.log('[BasicHandler] File을 데이터 URL로 변환'); return await this.fileToDataUrl(input); } throw new Error('지원하지 않는 입력 타입입니다'); }}// 이미지 업로드 프록시class ImageUploadProxy { constructor(config, baseHandler) { this.config = config; this.baseHandler = baseHandler; // 프록시 핵심: 기본 핸들러를 감쌈! } async handle(input) { console.log('[Proxy] input 받음:', input instanceof File ? input.name : input); // File이면 업로드 처리 if (input instanceof File) { console.log('[Proxy] File 업로드 시작'); // 검증 if (!this.validateFile(input)) { throw new Error('파일 검증 실패'); } try { this.config.onUploadStart?.(); // 업로드해서 URL 획득 const url = await this.uploadToServer(input); console.log('[Proxy] 업로드 완료, URL을 baseHandler에게 전달:', url); this.config.onUploadSuccess?.(url); // baseHandler에게 URL 전달 (프록시 패턴 핵심!) return await this.baseHandler.handle(url); } catch (error) { console.error('[Proxy] 업로드 실패:', error); this.config.onUploadError?.(error.message); throw error; } } // URL이면 그냥 baseHandler에게 바로 전달 console.log('[Proxy] URL이므로 baseHandler에게 바로 전달'); return await this.baseHandler.handle(input); } validateFile(file) { const { allowedExtensions, maxFileSize } = this.config; const extension = file.name.split('.').pop().toLowerCase(); if (!allowedExtensions.includes(extension)) { const error = `지원하지 않는 파일 형식입니다. (지원: ${allowedExtensions.join(', ')})`; this.config.onUploadError?.(error); return false; } if (file.size > maxFileSize) { const error = `파일 크기가 너무 큽니다. (최대: ${maxFileSize / 1024 / 1024}MB)`; this.config.onUploadError?.(error); return false; } console.log('[Proxy] 파일 검증 통과'); return true; } async uploadToServer(file) { return new Promise((resolve) => { setTimeout(() => { const mockUrl = `${this.config.uploadUrl}/images/${Date.now()}_${file.name}`; resolve(mockUrl); }, 1500); }); }}프록시 패턴은 기존 객체를 건드리지 않고 기능을 추가하기 좋아요. 그래서 데코레이터 패턴과 같다고 생각할 수 있어요. 데코레이터 패턴은 객체의 원래 기능은 유지하면서 여러 추가 기능을 동적으로 추가하는 것이 주 목적이에요. 하지만 프록시 패턴은 객체의 접근에 대한 제어가 주 목적이고 보통 여러 겹으로 감싸서 사용하진 않아요.
이제 프록시 패턴의 장단점에 대해서 알아봐요.
장점
단일 책임 원칙(SRP)을 더 잘 지킬 수 있다.(RealObject에 추가적인 접근 제어 코드 등이 들어가지 않음)
개방 폐쇄 원칙(OCP)을 더 잘 지킬 수 있다.(RealObject 코드 수정없이 Proxy를 추가하여 접근 제어 기능을 더한다.)
접근 제어뿐만이 아니라, RealObject의 함수 실행 전후, 실패 여부 등의 로깅이나 캐싱 등의 부가작업에도 좋다.
단점
프록시가 추가되며 프록시 내부의 코드 구현을 위해서라도 코드양이 방대해진다.
프록시를 사용하는 객체(인스턴스)가 많이 생성되면 성능 문제가 생길 수 있다.
프록시 패턴은 객체에 대한 접근을 제어하기 위한 강력한 디자인 패턴이에요. 핵심은 기존 객체를 수정하지 않고도 부가적인 기능을 추가할 수 있다는 점이에요.
개방-폐쇄 원칙(OCP)과 단일 책임 원칙(SRP)을 지키면서 객체의 접근을 제어할 수 있게 해줘서 기존 코드를 건드리지 않고도 검증, 로깅, 캐싱 등의 기능을 추가할 수 있어서 유지보수성이 좋아요. 다만 프록시가 많아지면 코드가 복잡해지고 성능 문제가 생길 수 있으니, 정말 필요한 곳에만 사용하는 것이 좋아요. 프론트엔드에서 React의 경우에는 Suspense 컴포넌트가 프록시 역할을 한다고 볼 수 있어요.
만약 여러분이 객체의 접근을 제어하고 싶으면 프록시 패턴의 사용을 고려해보세요. 물론 언제나 오버 엔지니어링인지 생각해 보시고요!