이 문서에서는 다익스트라 알고리즘의 개념과 작동 방식과 프로그래머스의 [미로 탈출] 문제를 설명해요.
다익스트라 알고리즘은 그래프의 한 정점에서 다른 모든 정점까지의 최단 경로를 찾는 알고리즘이에요.
컴퓨터 네트워크, 내비게이션 등 경로 탐색이 필요한 여러 분야에서 사용할 수 있어요.
다익스트라 알고리즘은 다음과 같은 핵심 개념을 기반으로 해요.
가중치 그래프 : 간선마다 음수가 아닌 가중치가 존재하는 그래프
출발점 : 최단 경로를 시작할 노드
거리 배열 : 각 노드 사이의 최단 거리
우선순위 큐 : 방문할 노드 중 가장 누적 비용이 적은 순으로 정렬하는 큐
정점의 개수를 V, 간선의 개수를 E라고 할 때, 다익스트라 알고리즘의 시간 복잡도는 다음과 같이 계산해요.
우선순위 큐를 사용하는 경우 시간복잡도는 O(VlogV + ElogV)에요.
각 반복문마다 미방문 노드 중 출발점으로부터 현재까지 누적 최단 거리를 우선순위 큐로 갱신하는 데 O(VlogV) 시간이 걸려요.
각 노드마다 이웃한 노드의 최단 거리를 갱신하는 데 O(ElovV) 시간이 걸려요.
만약 음의 가중치가 존재하는 경우 벨만-포드 알고리즘을 사용 해야해요.
다익스트라 알고리즘은 보통 다음의 절차를 따라요.
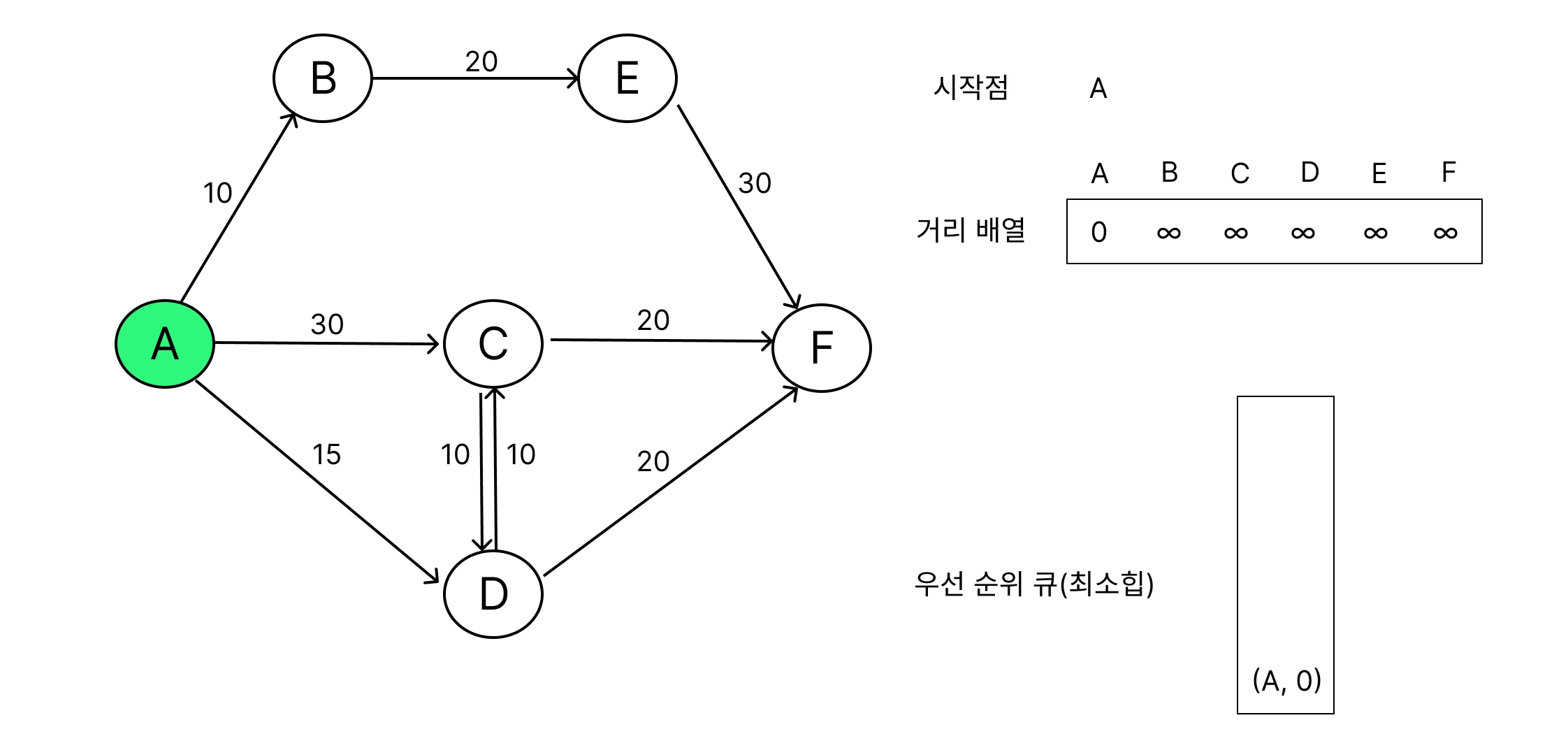
거리 배열 초기화
출발 노드의 거리는 0, 나머지 노드는 무한대로 설정해요.
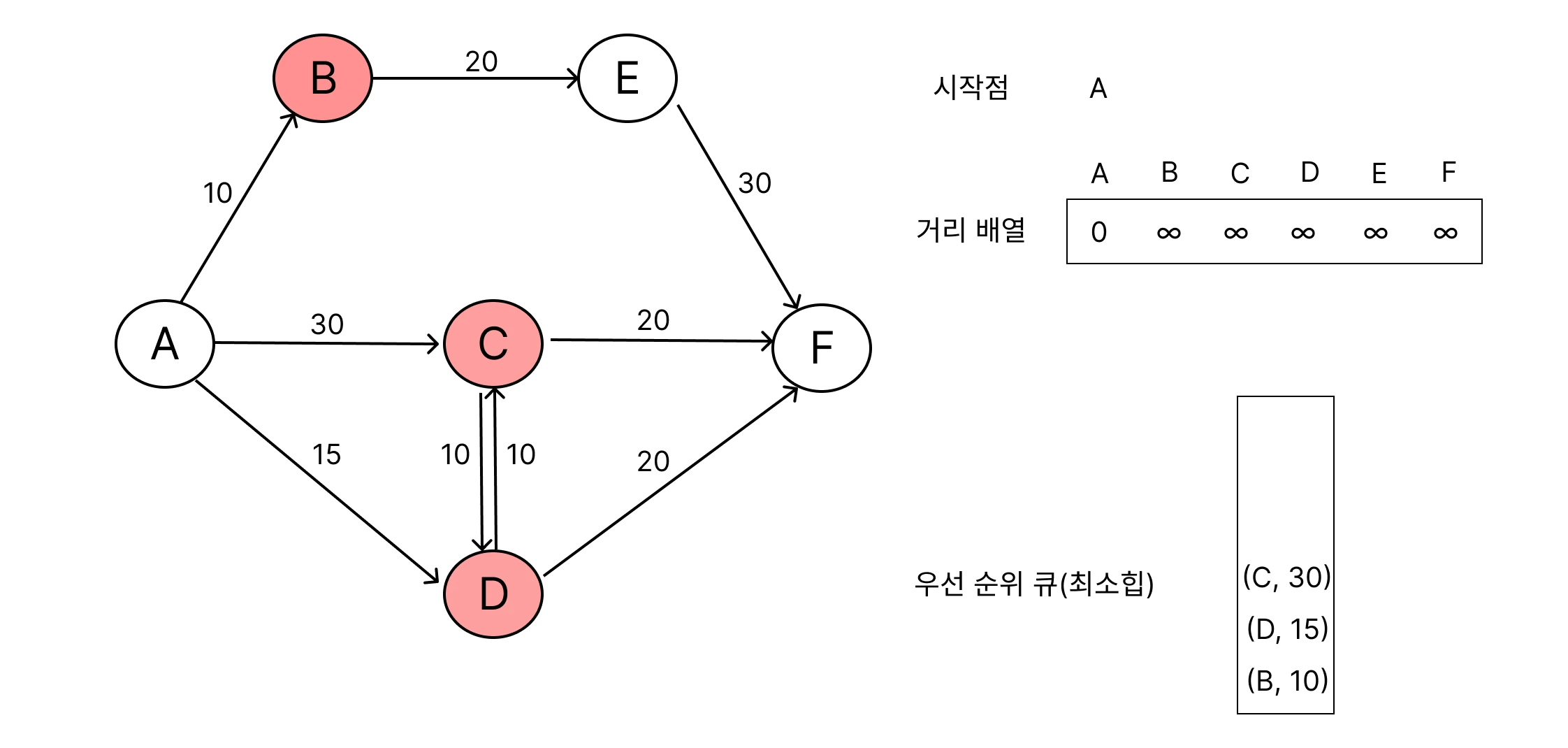
가장 가까운 노드 선택
큐의 출발점과 인접한 노드들을 선택하여 큐에 추가해요.
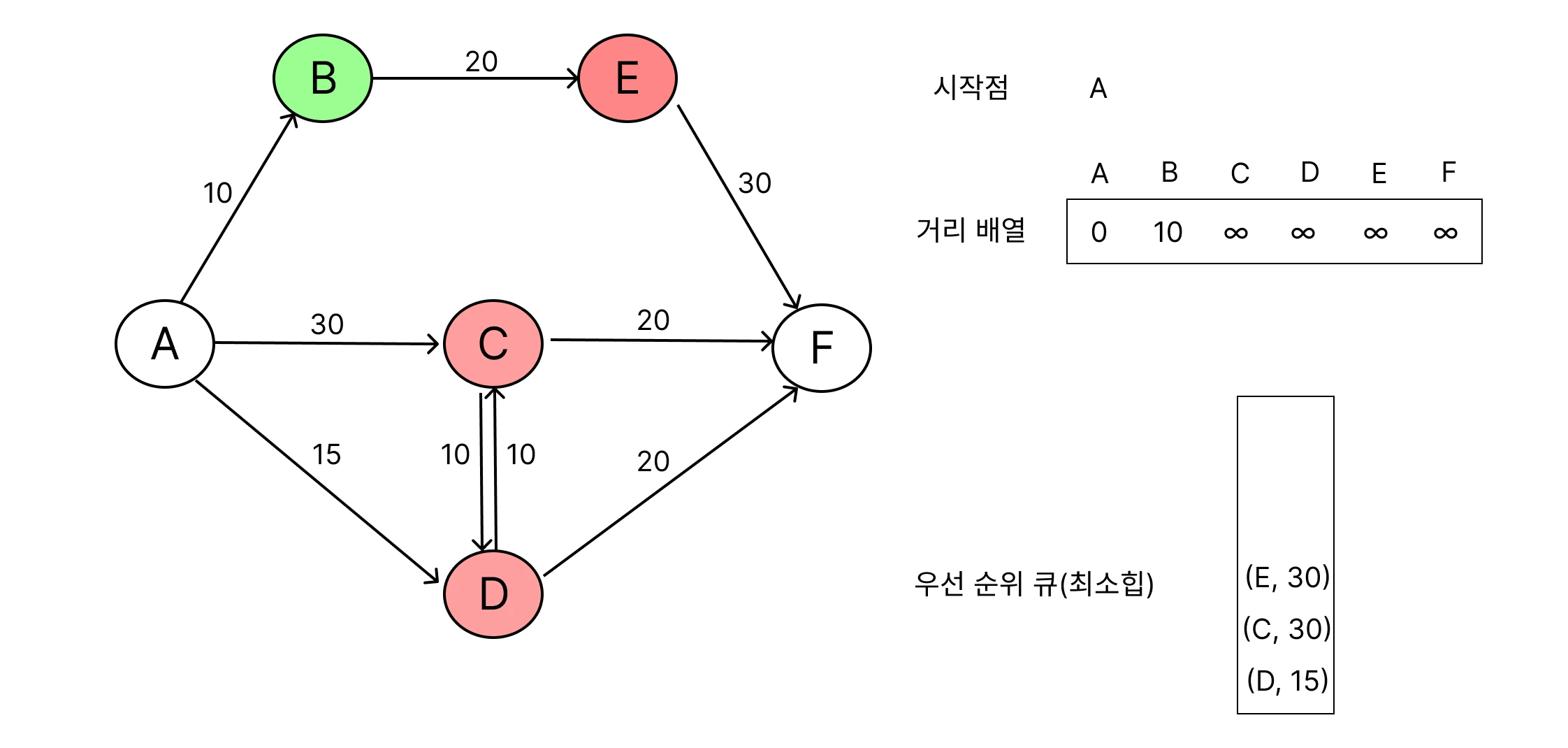
거리 갱신
선택된 노드의 인접 노드를 확인하면서, 출발점으로 부터 방문하지 않은 경로가 발견되면 계속 거리 배열 갱신을 해요.
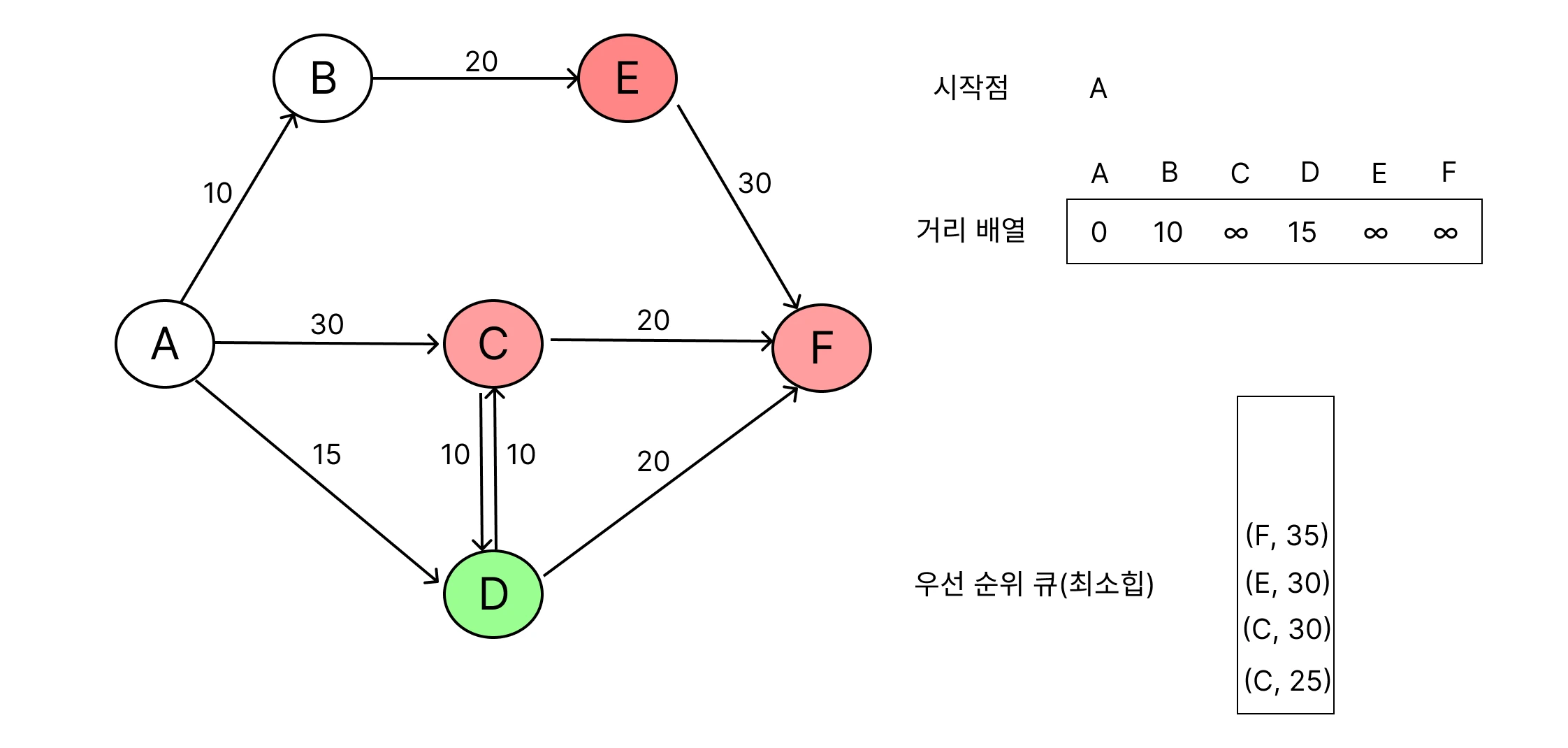
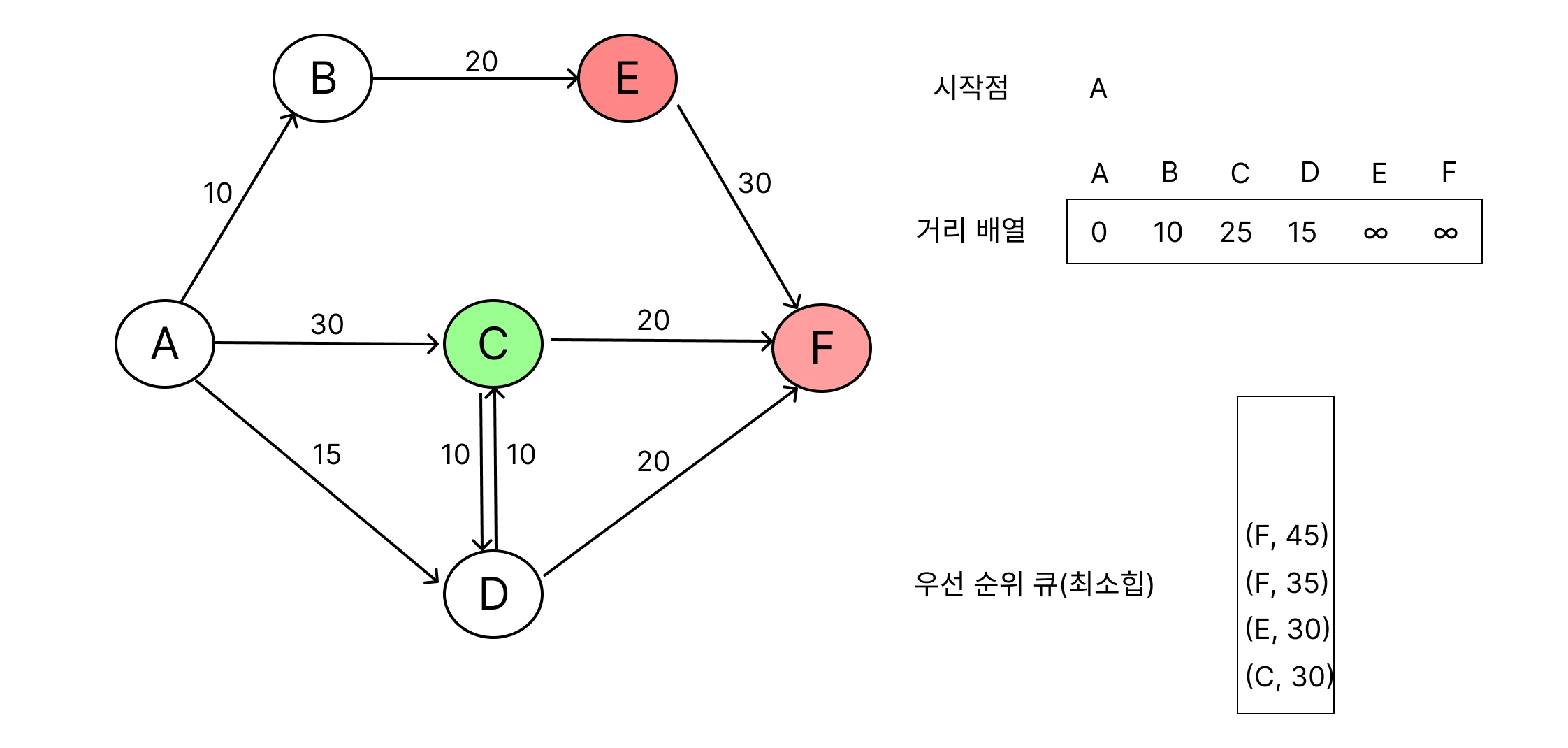
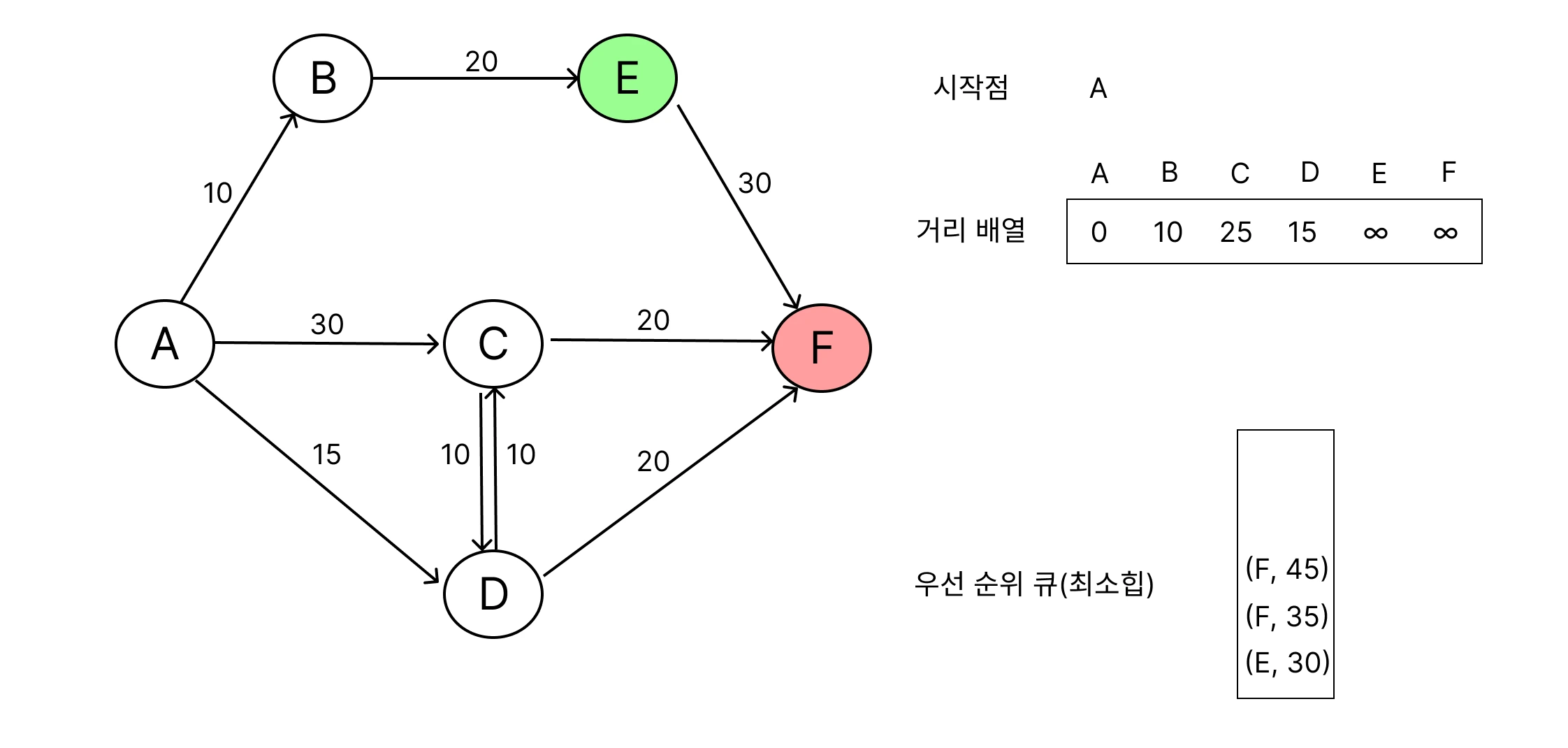
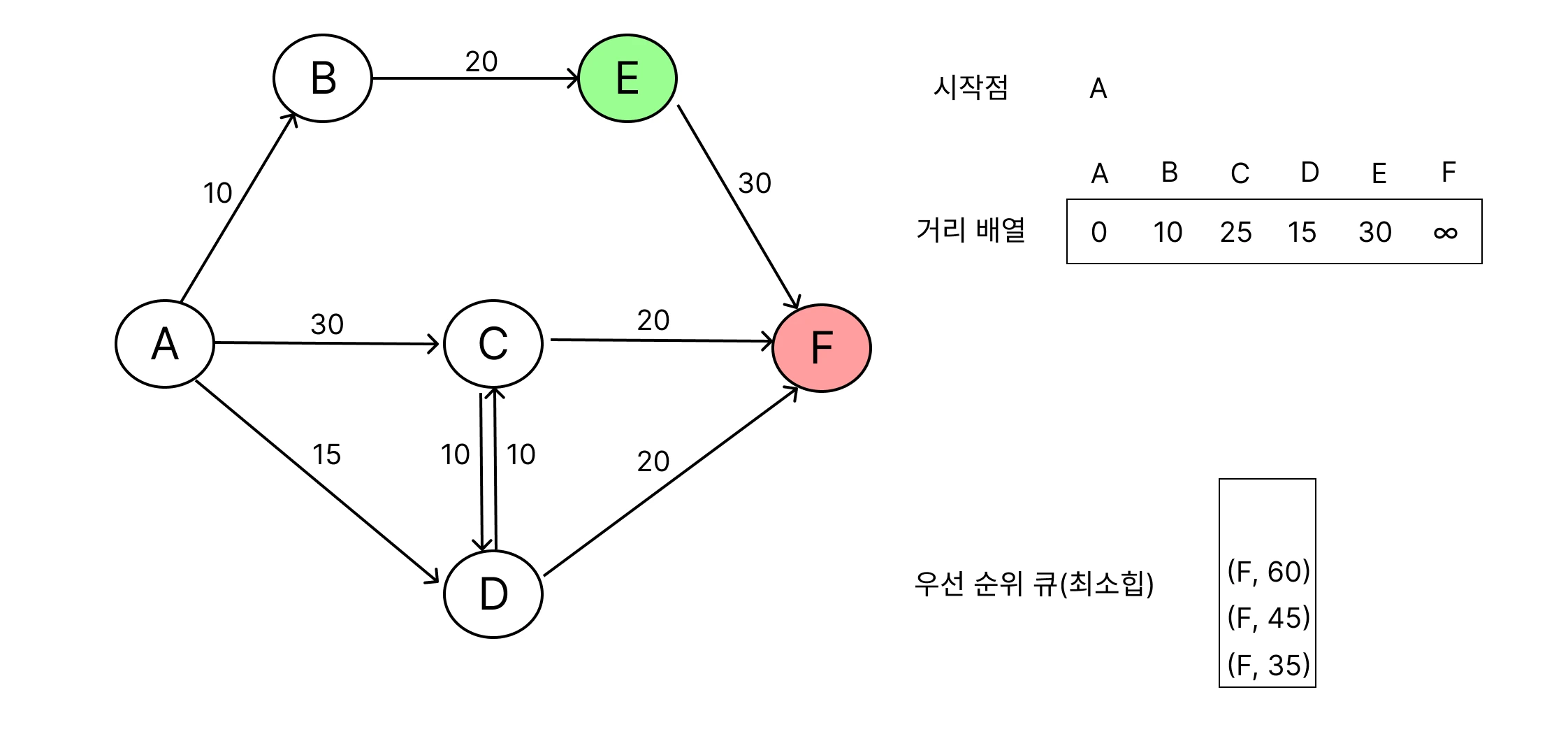
모든 노드가 방문되거나, 더 이상 갱신할 경로가 없을 때 알고리즘 종료해요.
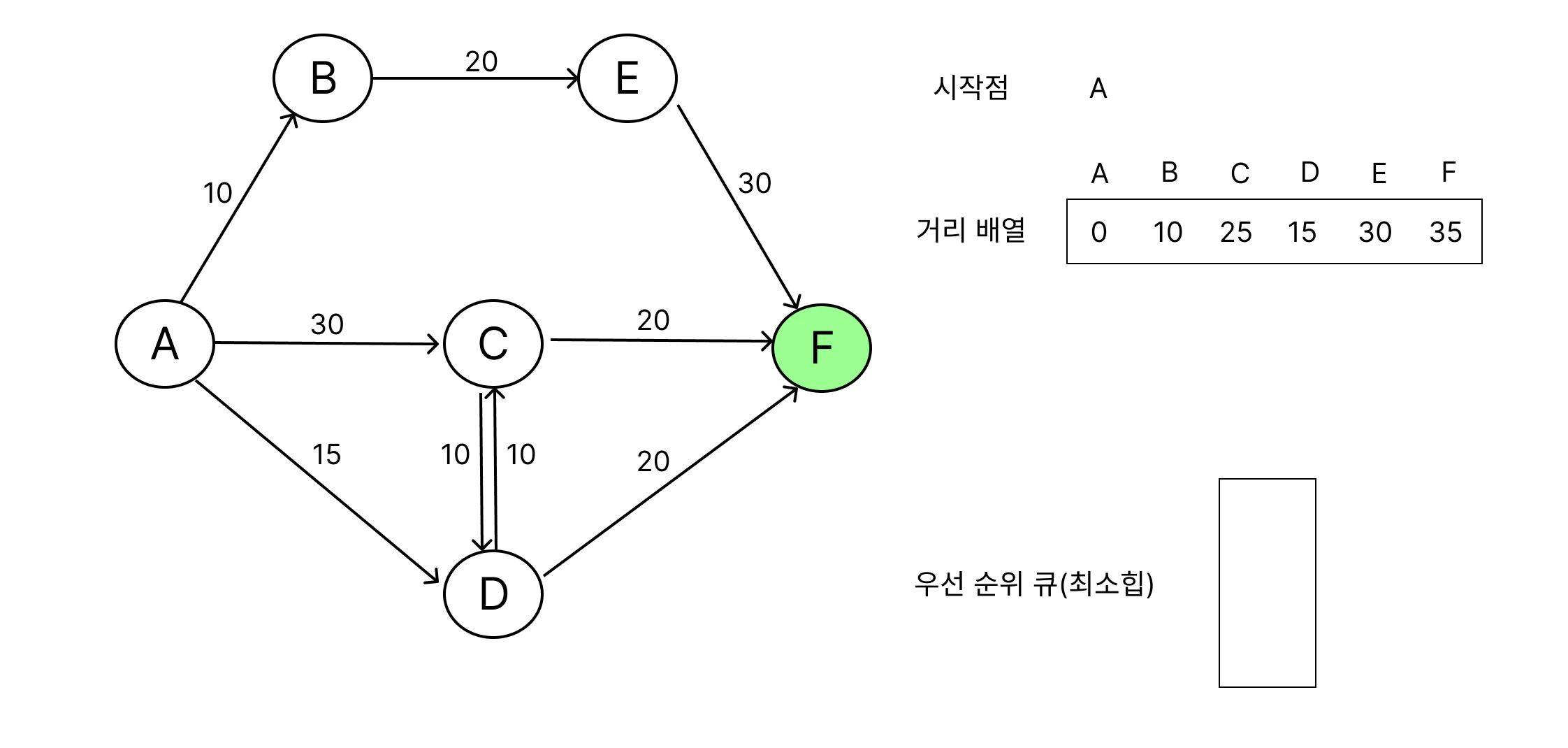
이 과정에서 더 짧은 누적거리를 가진 경로를 먼저 탐색하기 위해 우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)를 사용하여, 먼저 방문한 노드의 누적 거리 값이 최단 거리 값이에요.
다익스트라 알고리즘은 우선순위 큐가 아니더라도 계속 sort 함수를 실행하여 구현할 수 있어요. 하지만 시간복잡도가 좋지 않기 때문에 우선순위 큐를 활용해야 해요. 그래서 자바스크립트에서 효율적인 우선순위 큐를 구현할 수 있어야 해요. 우선순위 큐 예시 코드를 보여드릴 게요.
class PriorityQueue { constructor(comparator = (a, b) => a > b) { this.heap = []; this.comparator = comparator; // boolean comparator } size() { return this.heap.length; } isEmpty() { return this.size() === 0; } peek() { return this.heap[0]; } push(value) { this.heap.push(value); this._heapifyUp(); } pop() { if (this.isEmpty()) return null; const top = this.peek(); const last = this.heap.pop(); if (!this.isEmpty()) { this.heap[0] = last; this._heapifyDown(); } return top; } _heapifyUp() { let index = this.size() - 1; const element = this.heap[index]; while (index > 0) { const parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2); const parent = this.heap[parentIndex]; if (!this.comparator(element, parent)) break; this.heap[index] = parent; index = parentIndex; } this.heap[index] = element; } _heapifyDown() { let index = 0; const length = this.size(); const element = this.heap[0]; while (true) { const leftIndex = 2 * index + 1; const rightIndex = 2 * index + 2; let swapIndex = null; if (leftIndex < length && this.comparator(this.heap[leftIndex], element)) { swapIndex = leftIndex; } if ( rightIndex < length && ((swapIndex === null && this.comparator(this.heap[rightIndex], element)) || (swapIndex !== null && this.comparator(this.heap[rightIndex], this.heap[leftIndex]))) ) { swapIndex = rightIndex; } if (swapIndex === null) break; this.heap[index] = this.heap[swapIndex]; index = swapIndex; } this.heap[index] = element; }}
미로 탈출 문제에서 어떻게 다익스트라 알고리즘을 이용하여 문제를 풀었는지 코드를 보여드릴게요. 문제 설명은 길어서 별도 링크를 첨부할게요.
문제 설명 : 출발지에서 목적지까지 갈 수 있는 최단 거리 값을 구해야 해요. 노드는 일반 노드와 함정 노드가 있어요.
문제 핵심 :
다익스트라 알고리즘으로 출발지 X에서 목적지 Y까지의 거리를 구해야해요.
간선에는 방향이 존재해요.
A노드에서 B노드 사이에는 여러 개의 간선이 존재할 수 있어요.
노드에는 함정인 노드가 존재하고, 함정인 노드에 도착하면 함정 노드에 연결된 모든 간선의 방향이 반대로 바껴요.
출발지와 도착지는 함정 노드가 아니에요.
항상 출발지부터 도착지까지 도착이 가능해요.
풀이 핵심:
출발지 X로부터 전체 노드의 거리를 구하는 것이 아닌 특정 X 노드와의 거리만 구하면 종료해야해요.
A노드와 B노드 사이의 간선은 방향별로 최소값인 간선만 남겨야해요.
도착지가 없는 경우는 생각하지 않아도 되요.(못찾는 예외 처리가 필요 없어요.)
함정이 있기 때문에 같은 노드를 2번 밟는 경우가 생겨요.
간선이 바뀌는 노드들을 알기위해 노드, 간선 정보에 더해서 추가적인 상태값 저장이 필요해 보여요.
아래는 저가 처음 정답으로 제출한 코드에요. 급하게 푸느라 변수명부터 모두 엉망이네요. 위의 [3. 우선순위 큐]와 아래 코드의 우선순위 큐의 다른 점은 literal object로 구현했어요. 속도는 두 방법 모두 비슷하게 나오긴 했는데, V8 엔진 최적화에서 literal object가 더 안좋을 수 있다고 해요.(아마도 V8 엔진의 최적화 방식에 따라 같은 타입의 반복이 아니기 때문에 타입 템플릿 캐싱이 일어나지 않을 것이라 개인적으로 추측해요. 틀릴 수도 있으니 직접 학습해 보세요.)
class PriorityQueue { constructor(oper) { this.items = {}; this.tail = 0; this.oper = oper; } push(item) { const pushIndex = this.tail++; this.items[pushIndex] = item; this.heapUp(pushIndex); } pop() { if (this.isEmpty()) return undefined; const item = this.items[0]; const lastIndex = --this.tail; [this.items[0], this.items[lastIndex]] = [this.items[lastIndex], this.items[0]]; delete this.items[lastIndex]; if (!this.isEmpty()) this.heapDown(0); return item; } isEmpty() { return 0 === this.tail; } size() { return this.tail; } getParentIndex(index) { const parentIndex = Math.floor((index-1)/2); if(parentIndex < 0) return null; return parentIndex; } swapParent(index) { const parentIndex = Math.floor((index-1)/2); if(parentIndex < 0) return null; [this.items[index], this.items[parentIndex]] = [this.items[parentIndex],this.items[index]] } heapUp(index) { const item = this.items[index]; const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index) if(parentIndex === null) return; const parent = this.items[parentIndex]; if(this.oper(item, parent)){ this.swapParent(index); this.heapUp(parentIndex); } } heapDown(index) { const item = this.items[index]; const lIndex = index*2+1; const rIndex = index*2+2; if(this.tail <= lIndex) return; if(this.tail <= rIndex) { if(this.oper(this.items[lIndex],item)) [this.items[lIndex], this.items[index]] = [this.items[index], this.items[lIndex]] return this.heapDown(lIndex); } if(this.oper(this.items[lIndex],this.items[rIndex])) { if(this.oper(this.items[lIndex],item)) { [this.items[lIndex], this.items[index]] = [this.items[index], this.items[lIndex]] return this.heapDown(lIndex); } } else { if(this.oper(this.items[rIndex],item)) { [this.items[rIndex], this.items[index]] = [this.items[index], this.items[rIndex]] return this.heapDown(rIndex); } } }}// [현재 위치, 이동 거리]function solution(n, start, end, roads, traps) { const MAP = Array.from(Array(n+1),()=>Array(n+1).fill(0)) const visited = Array.from(Array(n+1),()=>[Math.infinite, Math.infinite]) roads.forEach((road)=>{ if(MAP[road[0]][road[1]] === 0) MAP[road[0]][road[1]]=road[2] else if(MAP[road[0]][road[1]] > road[2]) MAP[road[0]][road[1]] = road[2]; }) const queue = new PriorityQueue((item1,item2) => (item1[1] < item2[1])); queue.push([start,0,0,{},{}]) const trapsDict = traps.reduce((prev, trap)=>({...prev,[trap]:true}), {}) const answer = dik(queue, start, end, MAP, visited, trapsDict); return answer;}function dik(queue, start, end, Map, visited,traps) { const current = queue.pop(); // [위치, 이동 거리, 횟수, trapped] const [pos,dis,count,trapped,visited2] = current; const isTrap = traps[pos]; if(pos === end) return dis; if(count >= 2) return dik(queue, start, end, Map, visited, traps); if(dis > visited[pos][count]) return dik(queue, start, end, Map, visited, traps); visited[pos][count] = dis; const visitedCopy = {...visited2} if(visitedCopy[pos]) { visitedCopy[pos] += 1; } else { visitedCopy[pos] = 1; } const newTrapped = {...trapped}; if(isTrap){ newTrapped[pos] = newTrapped[pos]? 2: 1 } const newMap2 = [...Map[pos]]; if(isTrap && newTrapped[pos]!==2) { for(let i=1; i<newMap2.length; i++) { newMap2[i] = Map[i][pos]; } } Object.keys(trapped).forEach((trap)=> { if(newMap2[trap] === Map[trap][pos]) newMap2[trap] = Map[pos][trap]; else newMap2[trap] = Map[trap][pos]; }) newMap2.forEach((to,index)=> { if(to) { const visitTrapCount = newTrapped[index] ?? 0; const visitCount = visitedCopy[index] ?? 0; if(visitTrapCount>1) return; if(visitCount >1) return; queue.push([index,to+dis,visitCount,newTrapped,visitedCopy]) } }) return dik(queue, start, end, Map, visited, traps);}위 코드를 더 깔끔하게 변수명이랑 바꿔볼게요.
class PriorityQueue { constructor(comparator = (a, b) => a > b) { this.heap = []; this.comparator = comparator; } size() { return this.heap.length; } isEmpty() { return this.size() === 0; } peek() { return this.heap[0]; } push(value) { this.heap.push(value); this._heapifyUp(); } pop() { if (this.isEmpty()) return null; const top = this.peek(); const last = this.heap.pop(); if (!this.isEmpty()) { this.heap[0] = last; this._heapifyDown(); } return top; } _heapifyUp() { let index = this.size() - 1; const element = this.heap[index]; while (index > 0) { const parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2); const parent = this.heap[parentIndex]; if (!this.comparator(element, parent)) break; this.heap[index] = parent; index = parentIndex; } this.heap[index] = element; } _heapifyDown() { let index = 0; const length = this.size(); const element = this.heap[0]; while (true) { const leftIndex = 2 * index + 1; const rightIndex = 2 * index + 2; let swapIndex = null; if (leftIndex < length && this.comparator(this.heap[leftIndex], element)) { swapIndex = leftIndex; } if ( rightIndex < length && ((swapIndex === null && this.comparator(this.heap[rightIndex], element)) || (swapIndex !== null && this.comparator(this.heap[rightIndex], this.heap[leftIndex]))) ) { swapIndex = rightIndex; } if (swapIndex === null) break; this.heap[index] = this.heap[swapIndex]; index = swapIndex; } this.heap[index] = element; }}// [현재 위치, 누적 거리, 방문 횟수, 활성화된 트랩 상태, 방문 기록]function solution(n, start, end, roads, traps) { const graph = Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => Array(n + 1).fill(0)); // [처음 노드 밟았을 때 최단 거리, 2번째 노드 밟았을 때 최단 거리] const distanceRecord = Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => [Infinity, Infinity]); // 그래프 초기화 roads.forEach(([from, to, cost]) => { if (graph[from][to] === 0 || graph[from][to] > cost) { graph[from][to] = cost; } }); const pq = new PriorityQueue((a, b) => a[1] < b[1]); pq.push([start, 0, 0, {}, {}]); const trapSet = traps.reduce((acc, trap) => ({ ...acc, [trap]: true }), {}); return dijkstra(pq, end, graph, distanceRecord, trapSet);}function dijkstra(pq, end, graph, distanceRecord, trapSet) { while (!pq.isEmpty()) { const current = pq.pop(); const [pos, totalDist, visitCount, activeTraps, visitHistory] = current; const isTrap = trapSet[pos]; if (pos === end) return totalDist; if (visitCount >= 2) continue; if (totalDist > distanceRecord[pos][visitCount]) continue; distanceRecord[pos][visitCount] = totalDist; // 방문 기록 업데이트 const newVisitHistory = { ...visitHistory }; newVisitHistory[pos] = (newVisitHistory[pos] ?? 0) + 1; // 트랩 활성화 상태 업데이트 const newActiveTraps = { ...activeTraps }; if (isTrap) { newActiveTraps[pos] = newActiveTraps[pos] ? 2 : 1; } // 현재 위치 기준 이동 가능한 간선들 const nextEdges = [...graph[pos]]; if (isTrap && newActiveTraps[pos] !== 2) { for (let i = 1; i < nextEdges.length; i++) { nextEdges[i] = graph[i][pos]; } } // 다른 트랩 영향 반영 Object.keys(activeTraps).forEach((trap) => { if (nextEdges[trap] === graph[trap][pos]) { nextEdges[trap] = graph[pos][trap]; } else { nextEdges[trap] = graph[trap][pos]; } }); // 이동 nextEdges.forEach((cost, nextPos) => { if (cost) { const trapVisitCount = newActiveTraps[nextPos] ?? 0; const nodeVisitCount = newVisitHistory[nextPos] ?? 0; if (trapVisitCount > 1) return; if (nodeVisitCount > 1) return; pq.push([nextPos, totalDist + cost, nodeVisitCount, newActiveTraps, newVisitHistory]); } }); } return -1; // 도달 불가능}위 코드에서 왜 이렇게 바꿨는지, 왜 안바꿨는지 해설을 추가해볼게요.
위 코드에서 다익스트라 알고리즘 설명과 다르게 구현한 부분이 있을까요??
네 애초에 이미 방문한 노드면 원래 우선순위 큐에 해당 노드를 안넣는게 더 빠를거라 생각합니다. 하지만 저는 함정 때문에 2번 방문하는 경우까지 생각하다 보니 미쳐 생각하지 못했던 것 같습니다. 여러분은 distanceRecord[nodeVisitCount][nextPos]가 이미 방문되었다면 아에 queue에 안넣게 구현하세요!! 그게 더 빠를거라 생각합니다.
activeTraps를 왜 별도로 함께 넘기나요?
newVisitHistory와 traps 정보만 가지고 발동된 함정들을 알 수 있지만, 발동된 함정을 찾는데 시간이 많이 거릴 수 있다고 생각해서 별도 Map 자료형으로 activeTraps를 갖도록 했습니다.
그래프 간선 정보를 N X M 배열로 갖는데 너무 메모리를 많이 차지 않을까요?
네 노드의 개수가 증가하면 메모리를 많이 차지합니다. 그래서 Map 자료형으로 노드 별로 가지는 간선을 갖도록 하면 메모리를 많이 아낄 수 있습니다. 하지만, 그러면 노드 간선 존재 여부를 확인해야 하기 때문에 배열의 index로 접근하는 것보다는 느릴 것입니다. trade off 관계에서 속도에 더 중점을 두었습니다.
다익스트라 알고리즘 처리를 heap이 빌때까지 수행하는 while문으로 바꾸셨는데 왜 바꿨나요?
function 재귀 함수는 함수가 호출될 때 마다 Stack 영역에 함수가 쌓이게 됩니다. 즉, while문은 Scope만 새로 생기면 되지만, 재귀 함수로 처리하면 함수가 실행될 때마다 실행 컨텍스트가 생겨야 하고 그만큼 더많은 비용이 생깁니다.
더 빠르게 처리할 수는 없을까요?
글쎄요?? 음 우선 생각나는 건 없네요. 비트연산 하기에는 너무 array가 긴 것들 만 있는 것 같고... ArrayBuffer를 사용하기에도 크기가 가변적인 자료형을 사용하기 때문에 안될 것 같아요. 굳이 찾으면 Worker를 사용하면 되려나요..? 잘 모르겠습니다.